As artificial intelligence matures, a key challenge persists: how can AI systems understand the meaning behind the data they process? In other words, how do we move from smart calculations to context-aware decisions?
The answer is increasingly pointing toward knowledge graphs—a technology that SAP is strategically integrating across its platforms to bring deeper understanding and real-time reasoning into enterprise AI.
What Are Knowledge Graphs?
At their core, knowledge graphs are networks of information that connect entities (like products, suppliers, and customers) with defined relationships (such as “orders from,” “located in,” or “approved by”). They allow machines to reason more like humans—making connections, asking questions, and explaining outcomes.
If you’re new to the concept, we explored this in depth in our previous article:
What Is a Knowledge Graph, and Why Is It the Brain Behind Modern AI?
SAP’s Vision: AI That Understands Business
SAP isn’t just adopting AI—it’s reimagining how AI operates inside business systems. Rather than focusing solely on statistical learning or generic models, SAP’s approach brings structured business understanding into the heart of AI systems.
To do that, SAP is integrating knowledge graphs across its AI-powered tools, products, and platforms.
Key SAP Technologies Using Knowledge Graphs
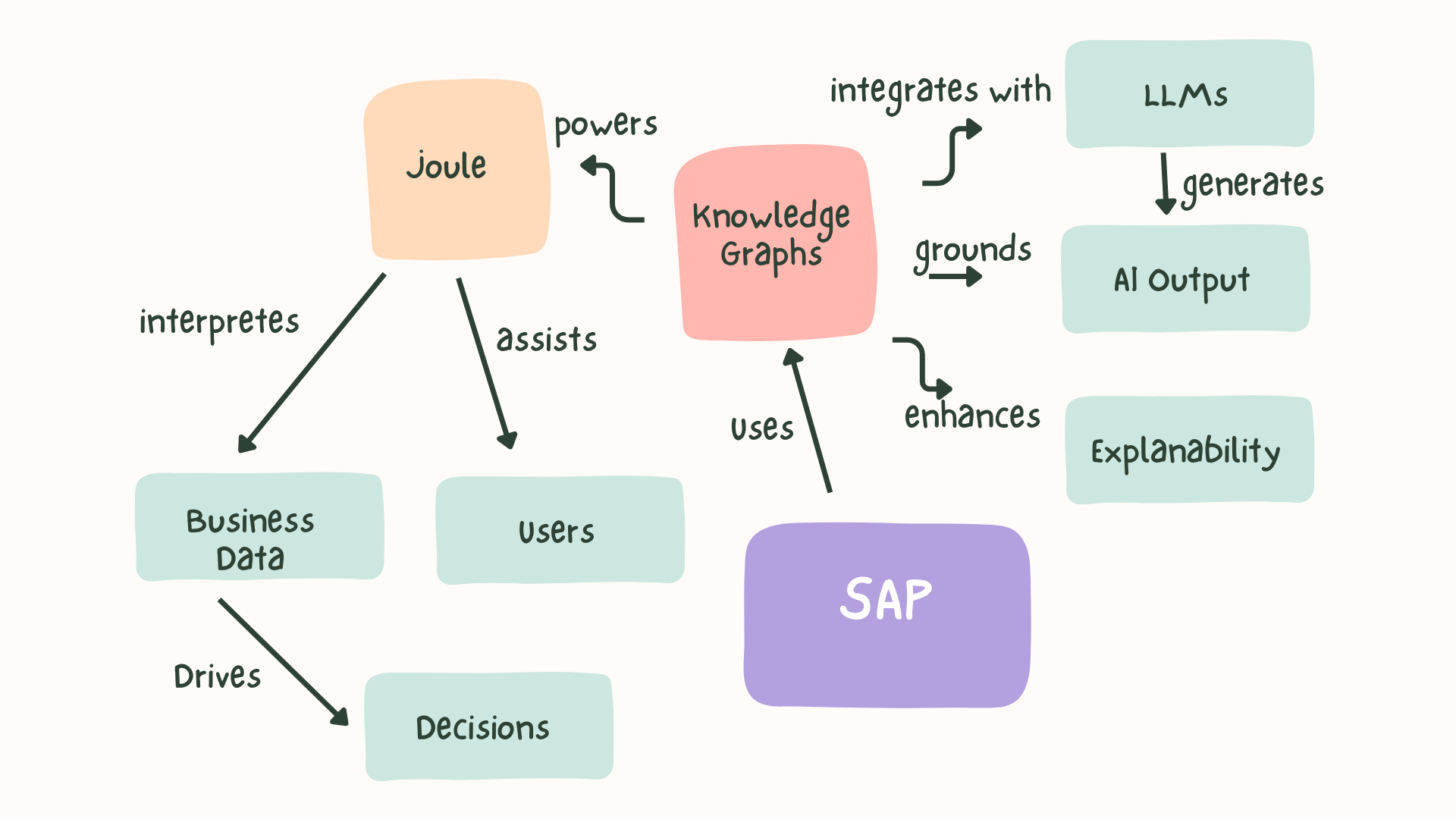
1. SAP Joule – AI That Knows the Business
Joule is SAP’s generative AI assistant. When users ask questions like, “Which of our suppliers performed best in Q1?”, Joule doesn’t just retrieve data—it understands context by connecting users, transactions, business goals, and terminology via a knowledge graph.
2. SAP Datasphere – Unified Semantic Modeling
Datasphere enables organizations to model enterprise data with semantic consistency. Using knowledge graph techniques, it links disparate data sources into a shared understanding—critical for making analytics and AI more trustworthy across business units.
3. SAP HANA Cloud – Real-Time Graph Querying
SAP HANA Cloud includes a graph engine that allows real-time analysis of complex relationships. Whether it’s fraud detection or supply chain analysis, users can now ask—and answer—questions that depend on deep, multi-hop connections between data points.
4. SAP Signavio – Process Intelligence Reimagined
Signavio helps companies map and optimize business processes. With knowledge graph capabilities, it can detect bottlenecks, dependencies, and inefficiencies based on how tasks, teams, and systems are interrelated.
Real-World Example: Supply Chain Insights
Imagine a manufacturer using SAP systems wants to assess supplier risk.
With knowledge graphs:
- Supplier performance is linked to location, delivery history, and quality reports
- Geopolitical events are connected to potential delays
- Recommendations are made in real time—based on context, not just rules
That’s not just automation. That’s AI with business reasoning.
SAP’s Hybrid AI Approach: Graphs + LLMs
SAP is exploring the fusion of knowledge graphs with large language models (LLMs) to form hybrid AI systems.
Why?
- LLMs (like GPT) are great at language generation
- Knowledge graphs excel at logic, structure, and explainability
By combining both, SAP aims to create AI that is not only insightful, but also accountable and transparent—a critical requirement for enterprise-grade systems.
SAP’s Position in the Evolving AI Ecosystem
While consumer tech companies focus on general-purpose AI, SAP is building business-specific intelligence grounded in real-world relationships.
This makes SAP’s approach uniquely suited for:
- AI-powered decision-making
- Transparent and auditable analytics
- Scalable, responsible automation
And at the heart of it all? Knowledge graphs—transforming enterprise data into something far more valuable: understanding.
What’s Next in the Series?
This article is part of our series exploring how knowledge graphs are transforming industries and technologies:
- What Is a Knowledge Graph?
- How SAP Is Powering AI with Knowledge Graphs (You are here)
- How Big Tech Uses Knowledge Graphs (Google, Microsoft, Amazon)
- Finance on Graphs: Risk, Fraud & Regulatory Insight
- The Future of Knowledge Graphs: From AI Agents to the Semantic Web
- Getting Started: Tools, Platforms, and How to Build One
Final Thoughts
SAP’s work with knowledge graphs is a glimpse into the future of enterprise AI—where systems don’t just automate, they understand.
If you’re considering how to build more intelligent, explainable, and business-aware AI, knowledge graphs may be the missing link.
Have thoughts or experiences using SAP’s graph-powered tools? I’d love to hear from you.